Hydropower is one of the oldest renewable resources and has been used for thousands of years. Hydroelectric power is classed as renewable energy due to the fact that it relies on the Earth’s natural water cycle to generate electricity. With its 90% efficiency in converting the kinetic energy to electricity and the fact that no fuels are burnt and no direct emissions are released into the atmosphere, it is often considered as a very clean form of electricity generation.
Hydroelectricity as a Renewable Energy Source
How much power does your UPS consume to do its job? – Part 1
August 27, 2020How To Select The Type Of Ups That Is Right For You
November 20, 2020So How Does Hydroelectric Energy Work?
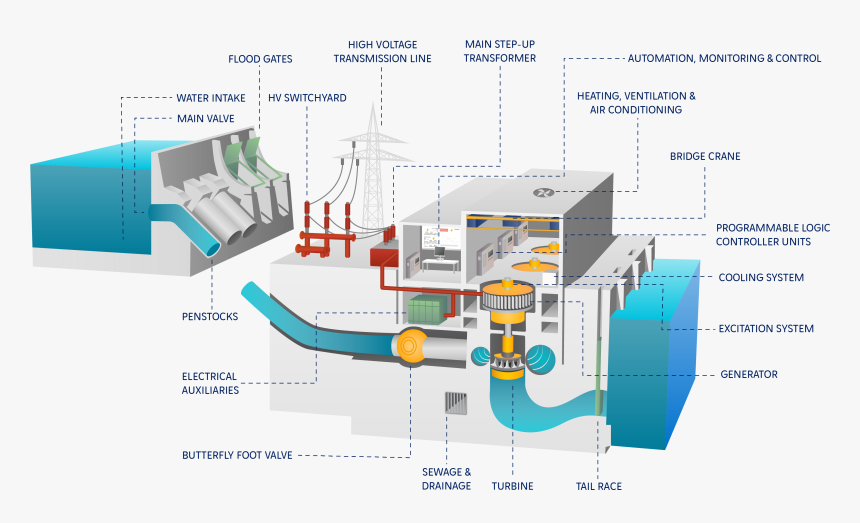
Most hydroelectric power plants have a reservoir of water, a gate or valve to control how much water flows out of the reservoir, and an outlet or place where the water ends up after flowing downward. Water gains potential energy just before it spills over the top of a dam or flows down a hill. The potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as water flows downhill. The water can be used to turn the blades of a turbine to generate electricity, which is distributed to the power plant’s customers.
Types of hydro and dams
There are several types of hydropower plants, and they are all powered by the kinetic energy of flowing water as it moves downstream.
- Run-of-river hydroelectricity (ROR) also known as run-of-the-river is where little or no water is stored or dammed. With there being no water storage at all is subject to seasonal river flows, thus the plant will operate as an intermittent energy source. To be a ROR the normal course of the river is not too materially altered in any way. They are normally small plants and have a low environmental impact.
- Pumped-Storage hydroelectricity (PSH) is a method of converting excess electrical energy into stored energy by pumping water vertically into a storage pond for later use. Low-cost surplus off-peak electric power is used to pump water from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher elevation.
- Reservoir hydroelectricity is the most common type of hydropower plant that uses a man-made dam on a river to store water in a reservoir. Water released from the reservoir flows through a turbine, spinning it, which in turn activates a generator to produce electricity. It is this damming of the river to create a reservoir that causes much of the environmental damage.
The Three Gorges Dam in China, which holds back the Yangtze River, is the largest hydroelectric dam in the world, in terms of electricity production. The dam is 2,335 meters (7,660 feet) long and 185 meters (607 feet) tall and has enough generators to produce 22,500 megawatts of power.
Nigeria is bestowed with large rivers and natural falls. The main water resources that provide rich hydropower potential are the Niger and Benue rivers and The total exploitable potential of hydropower is estimated at over 14,120 MW, of which only 2,062 MW produced today.
Nigeria has many hydroelectricity power plants the most popular of which are Kainji 760mw Jebba 578mw. The Ministry of Power and Ministry of Water Resources have established a partnership for the development of several existing hydropower plants, including the 30 MW Gurara 1, the 10 MW Tiga, 10 MW Oyan, the 8 MW Challawa and the 6 MW Ikere plants. In addition, the 700 MW Zungeru and the 40 MW Kashimbila hydropower plants are currently under construction.
A consortium from China constructing the 3,050 MW Mambilla plant began preparations after an agreement between the Minister of Power, Works and Housing of Nigeria and the consortium was signed last November. Nigeria’s so-called ‘Three Gorges Project’ will include four RCC gravity dams (Nya dam, Sumsum dam, Nghu dam, and Api weir) with over 700 km of transmission lines.
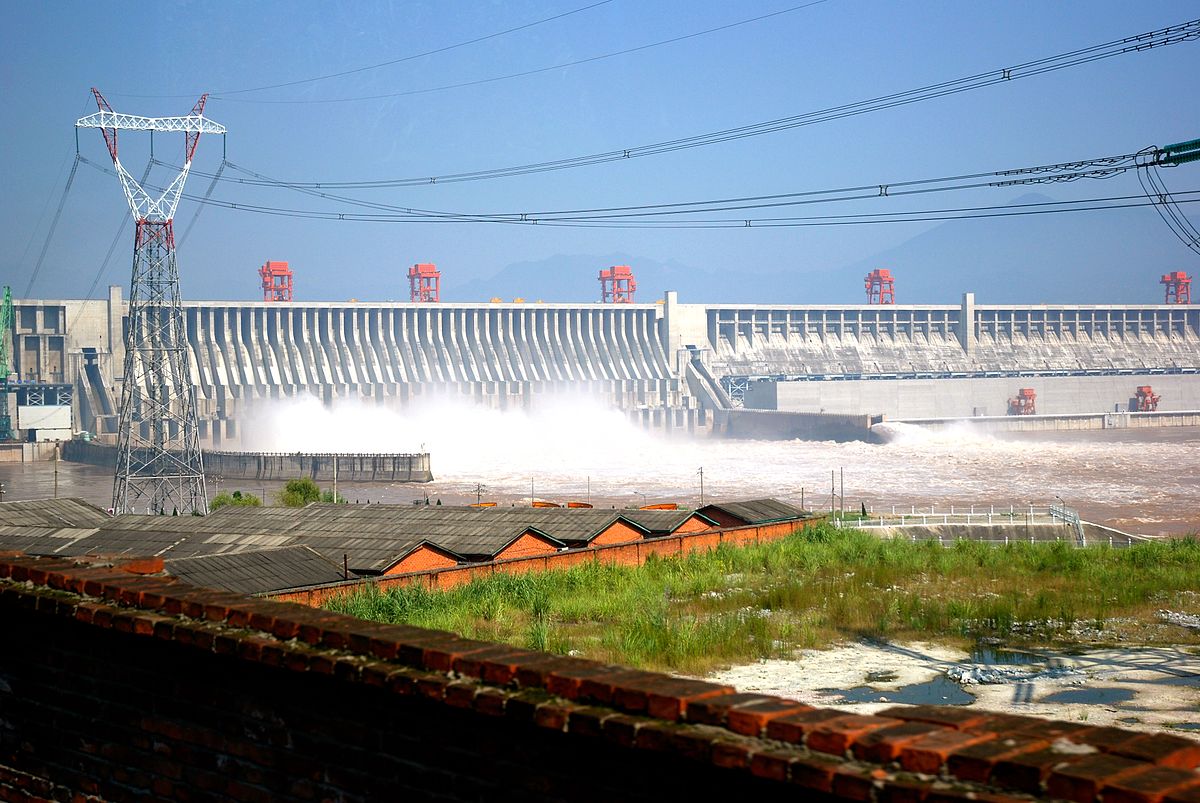


Benefits of hydropower
- Hydropower is fuelled by water, so it’s a clean fuel source, meaning it won’t pollute the air like power plants that burn fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas.
- Hydroelectric power is a domestic source of energy, allowing each state to produce its own energy without being reliant on international fuel sources.
- The energy generated through hydropower relies on the water cycle, which is driven by the sun, making it a renewable power source, making it a more reliable and affordable source than fossil fuels that are rapidly being depleted.
- Impoundment hydropower creates reservoirs that offer a variety of recreational opportunities, notably fishing, swimming, and boating. Most water power installations are required to provide some public access to the reservoir to allow the public to take advantage of these opportunities.
- Some hydropower facilities can quickly go from zero power to maximum output. Because hydropower plants can generate power to the grid immediately, they provide essential back-up power during major electricity outages or disruptions.

